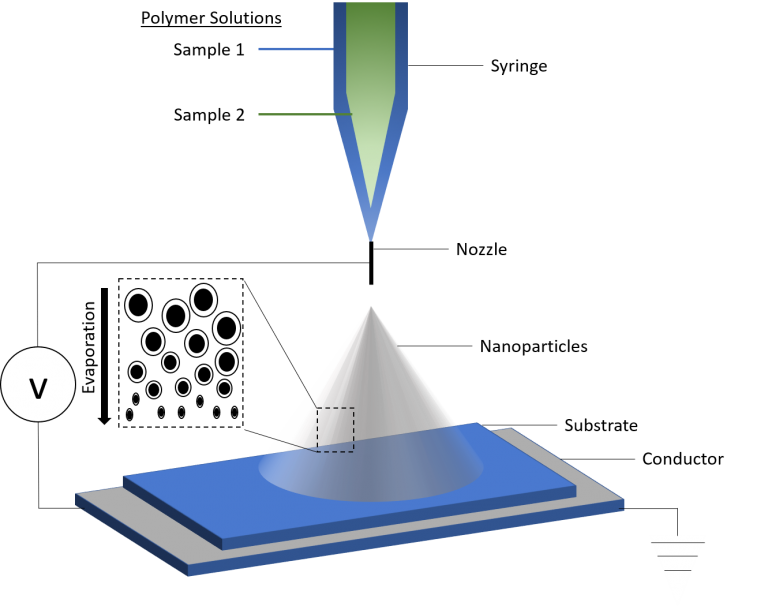
Electrospraying
Liquid atomization
About Electrospraying
Also known as electrohydrodynamic atomization, electrospraying is based on atomization of solvated polymers by electrical forces. Here, electrical forces overcome the forces of surface tension in the charged polymer solution and force a splitting chain reaction from droplet to nanoparticles. This produces spheres with a diameters ranging from 10nm <1000nm.
Summarised in three steps
- Acceleration of the polymeric solution and elongation into cone-jet by electrical shear stress
- Jet breakup into droplets due to interfacial instability
- Droplets repeatedly split to form nanoparticles as they dry
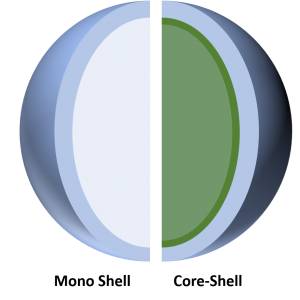
Coaxial Electrospraying
Coaxial electrospraying is a novel nanoencapsulation method that modifies the single-axial electrospray process by using a coaxial needle to deliver two liquids independently to delivers a core-shell morphology. These structures play a pivotal role in augmenting desirable pharmacokinetic properties by sustained and prolonged release of the bioactive as well as protecting it from harsh biological environments.